Business Hours (UTC+3)
Mon-Fri: 8 AM - 5 PM
Mon-Fri: 8 AM - 5 PM
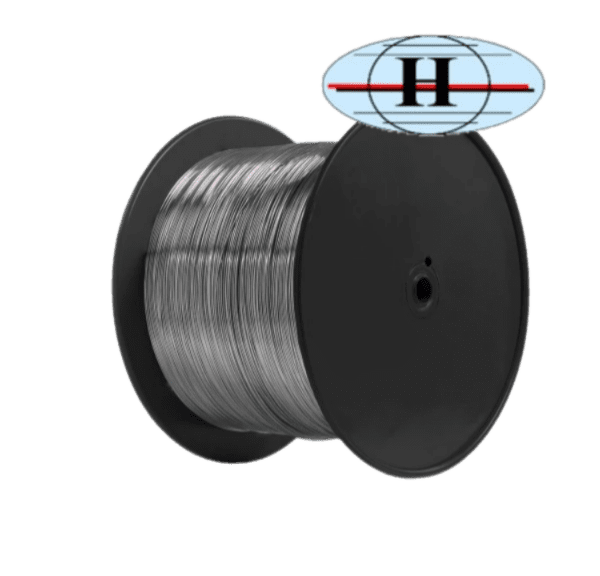
HARMS corrosion-resistant wire
High-quality slickline wire made of stainless steel alloy with an increased content of molybdenum. Designed for operation in aggressive fluids of oil and gas wells with a high content of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), chloride and carbon dioxide.
By clicking on the button, you consent to the processing of your personal data in accordance with the privacy policy
01
02
Direct equipment manufacturer
We guarantee the quality of our products

Certified equipment
Development according to drawings
Warranty service
Worldwide delivery
Corrosion-resistant stainless steel scraper wire is used as a part of LKI-Techno well logging winches, well slickline units (AIS), well dewaxing units (UDS, MDSA, Padus) and other equipment for round trip slickline conveyed well logging and testing operations, mechanical cleaning of the surface of tubing walls as well as downhole fluid sampling.
Technical Specifications
Due to nickel and nitrogen content UNIVERSAL wire has austenitic stability and a reduced tendency to form intermetallic phases during hot processing. Oil and gas are not corrosive substances but presence of water and oxygen, chlorides, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide in oil and gas accelerates pitting and stress related corrosion cracking.
Due to high content of chromium, molybdenum and nitrogen, the wire is highly resistant to pitting. Nickel content of 25 %, together with excellent resistance to local corrosion, makes UNIVERSAL wire highly resistant to corrosion cracking caused by stress and exposure to chlorine ions
UNIVERSAL wire made of an alloy conforming to ISO 15156-3: 2015, is used for the oil and gas industry, corrosion resistance index is equal to 47 PREN, (TÜV, S502)
Due to high content of chromium, molybdenum and nitrogen, the wire is highly resistant to pitting. Nickel content of 25 %, together with excellent resistance to local corrosion, makes UNIVERSAL wire highly resistant to corrosion cracking caused by stress and exposure to chlorine ions
UNIVERSAL wire made of an alloy conforming to ISO 15156-3: 2015, is used for the oil and gas industry, corrosion resistance index is equal to 47 PREN, (TÜV, S502)
Corrosion resistance
UNIVERSAL wire is tested and certified for minimum rated tensile strength. The permissible resistance is in the range of 80-90 % of the ultimate strength. This means that the Universal wire can withstand heavy loads without displaying permanent residual deformation effect.
Mechanical Properties
Photo Gallery
FAQs
Corrosion resistant wire is available in diameters of 1.83; 2.08 2.34; 2.74 and 3.18 mm.
Yes, we offer a 1 year warranty on HARMS corrosion resistant wire.
To order equipment and consult with our experts, you can contact us by phone, email or fill out the feedback form on our website. Our team will be happy to help you find a solution optimised for your needs.



